NVIDIA B200 GPU: Architecture, GB200 Comparison, and Practical Considerations for AI Teams
As artificial intelligence and large language models (LLMs) continue to advance, the demand for high-performance GPUs has grown tremendously. NVIDIA’s B200 GPU is one of the latest options designed to accelerate both AI training and inference. In this article, we’ll explore what makes B200 fast, how it compares to GB200, and practical considerations for choosing between buying or renting these GPUs.

Understanding the Architecture of B200
The B200 is built on NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture, optimized for large-scale AI computations. Its design focuses on increasing throughput, reducing bottlenecks, and supporting modern AI workloads.
| GPU Specifications | H200 SXM | B200 HGX | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computation | TF32 Tensor Core | 989 TFLOPS | 2,200 TFLOPS |
| FP16 Tensor Core | 1,979 TFLOPS | 4,500 TFLOPS | |
| BF16 Tensor Core | 1,979 TFLOPS | 4,500 TFLOPS | |
| FP8 Tensor Core | 3,958 TFLOPS | 9,000 TFLOPS | |
| INT8 Tensor Core | 3,958 TFLOPS | 9,000 TFLOPS | |
| FP4 Tensor Core | Unsupported | 18,000 TFLOPS | |
| Memory | GPU Memory | 141GB HBM3e | 180GB HBM3e |
| Bandwidth | 4.8 TB/s | 7.7 TB/s | |
| Interconnect | PCIe | 128 GB/s | 128 GB/s |
| NVLink | 900 GB/s | 1,800 GB/s |
The B200 delivers a step change in performance compared to the previous H200 due to several key improvements:
-
More Tensor Core Throughput: Across TF32, FP16, BF16, and FP8, the B200 provides roughly 2× the raw compute of the H200, reducing training time and inference throughput significantly.
-
New FP4 Precision: Blackwell introduces native FP4 tensor operations, achieving throughput to 18,000 TFLOPS for LLM inference.
-
Larger & Faster Memory: With 180 GB of HBM3e and 7.7 TB/s bandwidth, the B200 is able to support larger models and satruate its compute power.
-
Improved Interconnects: NVLink bandwidth doubles from 900 GB/s to 1,800 GB/s, improving scaling efficiency across multi-GPU systems.
B200 vs GB200: What’s the Difference?
While the B200 excels in single-node AI training, NVIDIA’s GB200 is optimized for multi-node, distributed environments, like data centers.
The NVIDIA DGX™ B200 is a unified AI platform for businesses at any stage of their AI journey. With eight Blackwell GPUs connected via fifth-generation NVIDIA® NVLink™, it delivers 3× training and 15× inference performance over previous-generation systems, handling workloads from LLMs to recommender systems and chatbots.
The GB200 compute tray features two Grace CPUs and four Blackwell GPUs, supports PCIe Gen 6 and liquid cooling, and delivers 80 petaflops of AI performance with 1.7 TB of fast memory. The GB200 NVL72 rack system connects 18 compute nodes via the NVIDIA NVLink Switch System with nine switch trays and cable cartridges, ensuring high-bandwidth, low-latency parallel processing for large-scale AI workloads.
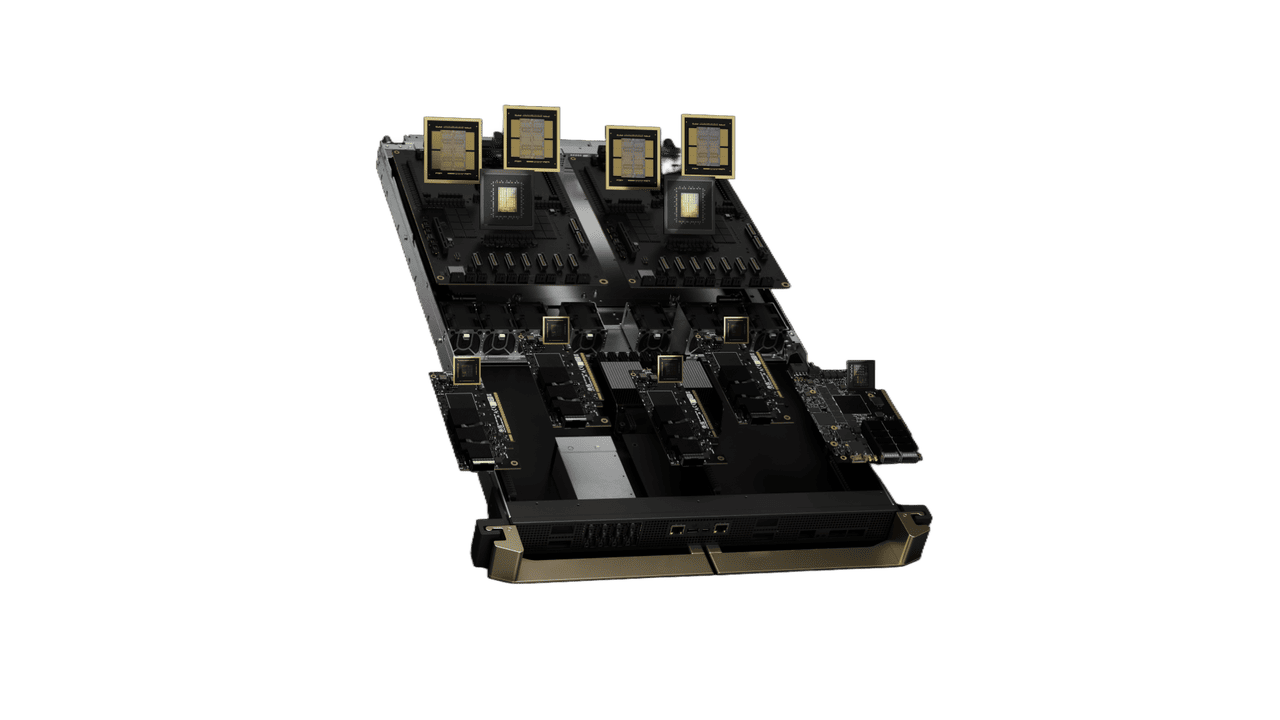
While both the DGX B200 and GB200 are powered by NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, they target slightly different deployment scenarios.
-
DGX B200: A turnkey, unified AI platform ideal for businesses seeking rapid deployment. Its eight interconnected GPUs provide consistent training and inference performance out of the box, making it perfect for enterprises running diverse AI workloads without building complex infrastructure.
-
GB200: A modular compute tray designed for large-scale, custom deployments. Each tray contains four GPUs and two Grace CPUs, integrates into the NVL72 rack for massive parallelism, and is best suited for organizations with the resources to build tailored clusters for high-performance AI training and inference.
In short:
-
B200 offers high performance with flexibility and cost efficiency.
-
GB200 Superchip integrates GPUs and CPU in a single package, delivering greater throughput and memory advantages for advanced workloads.
-
GB200 NVL72 scales this even further into a full rack solution, designed only for hyperscale AI.
For most enterprises, the B200 provides the optimal balance of performance and affordability. Platforms like HPC-AI.COM allow on-demand access to B200 GPUs, eliminating the need for massive upfront investment while still benefiting from state-of-the-art AI acceleration.
Buy or Rent B200: Practical Considerations
For AI teams, another common question is whether to purchase a B200 GPU or rent it through a cloud platform.
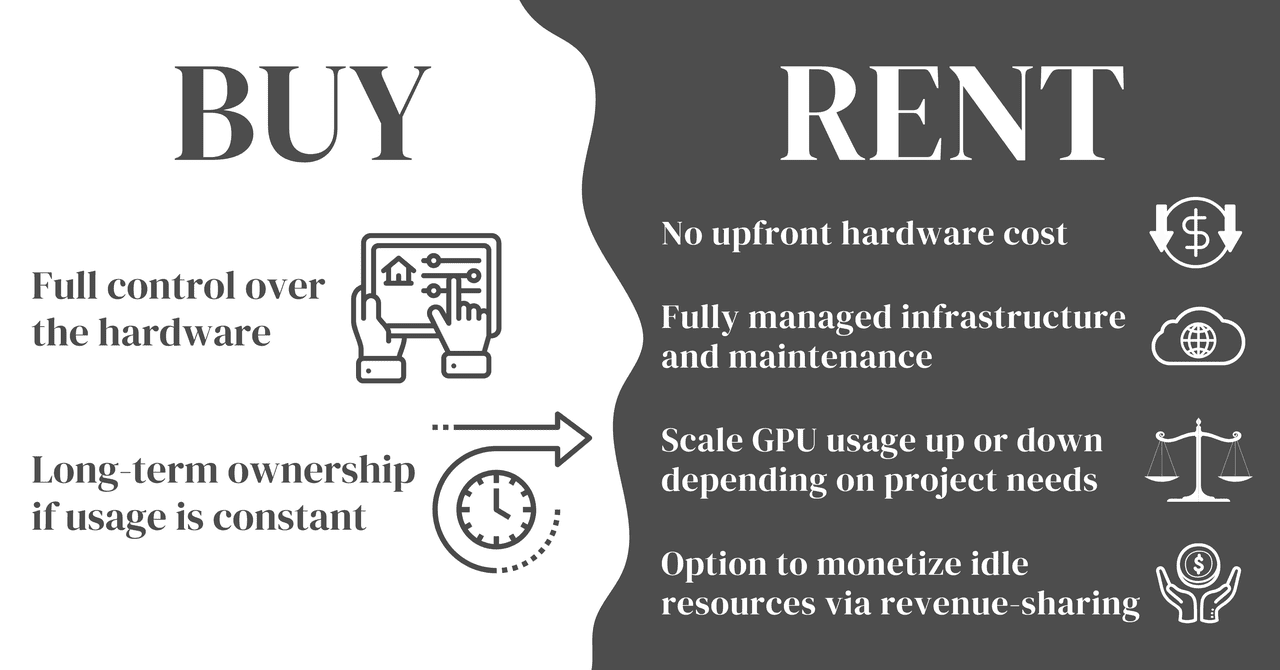
Buying a B200
Pros:
-
Full control over the hardware
-
Long-term ownership if usage is constant
Cons:
-
High upfront cost: approx. $500,000 per node (GPU + server + infrastructure)
-
Ongoing costs for electricity, maintenance, and IT support
-
Hardware may become outdated in a few years
Renting a B200
Cloud platforms like HPC-AI.COM offer flexible B200 GPU rental at $2.47/hr:
Pros:
-
No upfront hardware cost
-
Fully managed infrastructure and maintenance
-
Scale GPU usage up or down depending on project needs
-
Option to monetize idle resources via revenue-sharing
Cons:
- Hourly usage costs may add up for continuous, full-time workloads
Economic Perspective:
-
Renting is often more cost-effective for small teams or projects with variable workloads.
-
Purchasing makes sense only if GPUs are used heavily and continuously over several years.
Conclusion
The NVIDIA B200 delivers outstanding training and inference performance through high core count, high-bandwidth memory, multi-precision optimization, and high-speed interconnects. Compared to GB200, B200 excels in single-node performance, making it ideal for startups, research labs, and cloud platform users.
From an economic perspective, renting B200 through HPC-AI.COM allows teams to scale quickly, avoid high upfront costs, and focus on AI development instead of hardware management.
💡 Ready to accelerate your AI projects? Explore B200 rentals on HPC-AI.COM and start training immediately.
Reference:
https://nvdam.widen.net/s/nb5zzzsjdf/hpc-datasheet-sc23-h200-datasheet-3002446