Docker Container Guide
HPC-AI.COM manages cloud instances as containers using our proprietary ML engine. For users requiring Docker functionality, we provide Docker-in-Docker capabilities to build images and run GPU-enabled containers within your instance.
Getting Started
Enabling Docker Support
To activate Docker functionality:
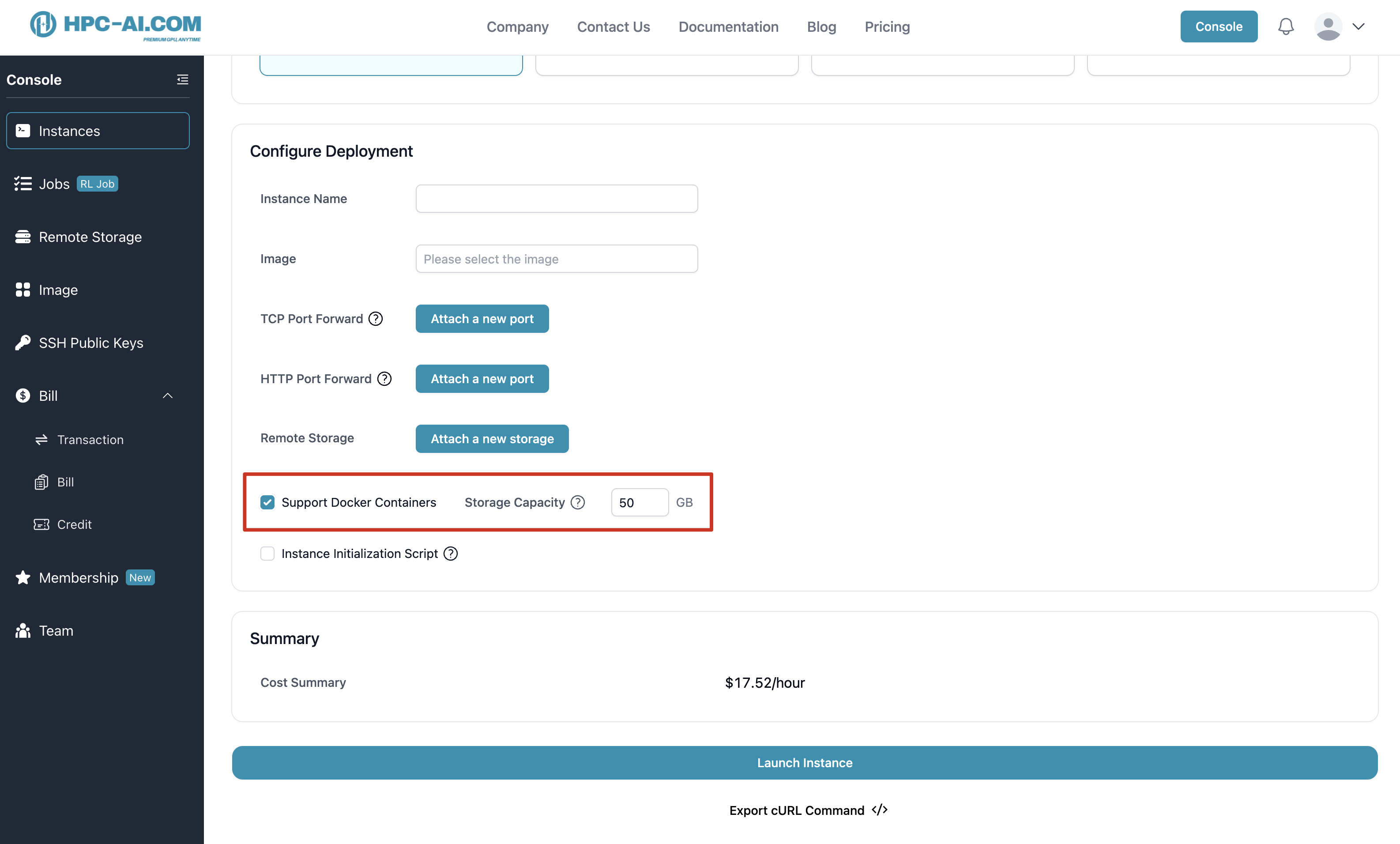
- Check the Support Docker option when creating a new instance
- Configure the required storage size for Docker operations
💡 Important Note: Docker storage is separate from your instance storage and persists when the instance is shut down.
Functionality Verification
Docker functionality is pre-installed on the platform, including both Docker Daemon and CLI tools.
Execute the following command to verify Docker is running properly:
# Check Docker version information
docker --version
docker version
# View Docker system information
docker info
# View all containers (including stopped ones)
docker ps -a
# View local images
docker images
📚 Reference: You can install additional Docker components as needed.For comprehensive installation instructions, consult the official Docker documentation.
Image Management
Building Custom Images
You can create custom images using either docker build or docker commit commands within your Docker-enabled cloud instance.
Example: Creating an Image with docker commit
# List running containers
root@notebook-instance:~# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
3c8b2aa1e6a2 ollama/ollama "/bin/ollama serve" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:11434->11434/tcp, [::]:11434->11434/tcp heuristic_saha
# Commit container changes to create new image
root@notebook-instance:~# docker commit 3c8b2aa1e6a2 my_ollama
sha256:3ba08852467f4b031e2166b6aa9f49bafead05f3349a81aa8bc3faebf188755f
# Verify the new image
root@notebook-instance:~# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
my_ollama latest 3ba08852467f About a minute ago 6.1GB
ollama/ollama latest 53f18253db46 25 hours ago 2.28GB
Exporting Images
Export your custom images as .tar files for offline distribution or backup:
# Export image to tar file
root@notebook-instance:/# docker save -o ~/dataDisk/my_ollama.tar my_ollama:latest
This allows you to transfer the image to other systems using docker load.
Container Operations
GPU Access
Enable GPU access within your containers by using the --gpus all flag during container creation.
Example: Running Llama2 with Ollama Container
# Check available images
root@notebook-instance:/# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
my_ollama latest 3ba08852467f 26 minutes ago 6.1GB
ollama/ollama latest 53f18253db46 25 hours ago 2.28GB
# Run container with GPU access
root@notebook-instance:/# docker run -d --gpus all -p 11434:11434 my_ollama
2614c3b596a80a24e5e0113a91d82c3c103750a9d895c465f55082d5ea85df38
# Access the container
root@notebook-instance:/# docker exec -it 261 bash
# Inside the container - pull and run model
root@3c8b2aa1e6a2:/# ollama pull llama2
root@3c8b2aa1e6a2:/# ollama run llama2
Storage Management for Large Models
⚠️ Storage Limit: Docker storage on this platform is capped at 100GB. For large models, use shared storage or data disks with volume mounting.
Example: Mounting Models to Data Disk
Step 1: Create a model directory on your data disk
root@notebook-instance:~# mkdir -p /dataDisk/ollama_models
Step 2: Create a Docker volume
root@notebook-instance:~# docker volume create --driver local \
--opt type=none \
--opt o=bind \
--opt device=/root/dataDisk/ollama_models/ \
ollama_models_volume
Step 3: Launch your application with the mounted volume
root@notebook-instance:~# docker run -d \
--name my_ollama \
-v ollama_models_volume:/root/.ollama \
-p 11434:11434 \
--gpus all \
ollama/ollama
Step 4: Access the container for debugging
root@notebook-instance:~# docker exec -it my_ollama bash
Resource Considerations
Performance Impact
When Docker is enabled, the cloud instance (main container) and internal containers share CPU and memory resources. If Docker functionality isn't required, consider creating instances without Docker support for optimal performance.
Storage Location
Docker images and container configurations are stored in /var/lib/docker/ on the cloud instance. This storage does not support online expansion.
Maintenance and Cleanup
When storage space becomes limited, use these cleanup commands:
# Remove stopped containers
docker container prune
# Remove unused images
docker image prune # Remove dangling images
docker image prune -a # Remove all unused images
# Remove unused volumes
docker volume prune
# Remove unused networks
docker network prune
# Clear build cache
docker builder prune
Best Practices
- Storage Planning: Monitor Docker storage usage regularly due to the 100GB limit.
- Volume Mounting: Use data disk mounting for large models and datasets.
- Resource Monitoring: Be aware of shared CPU/memory resources when running multiple containers.
- Regular Cleanup: Implement routine maintenance to prevent storage issues.
- Image Optimization: Use multi-stage builds and minimize image layers to reduce storage consumption.